
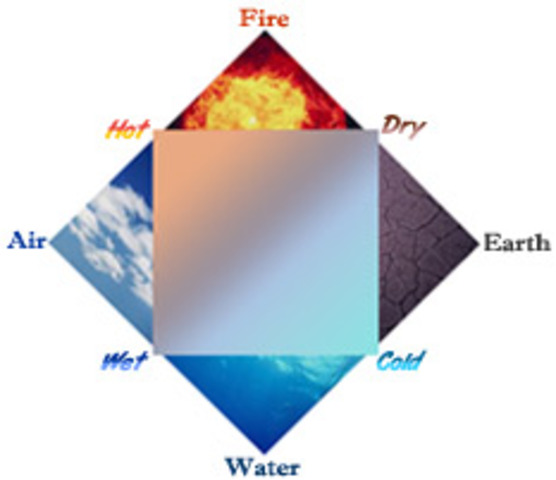
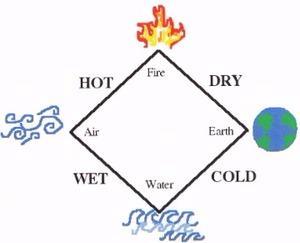
Many consider Democritus to be the "father of modern science". Plato is said to have disliked him so much that he wished all his books burnt. here aristotle argues that the amount of change in the object being moved will be in direct proportion to the amount of power applied to it by the agent, and in inverse proportion to the resistance to that change, which comes from the quantity of the body being moved and the density of the physical medium through which it is moving. Ernest Rutherford’s gold foil experiment involved a particle emitter, a round detecting screen with a slit in it and a slip of gold foil in the middle. Many chemists and philosophers argued Aristotle and believed in atomic theory. His beliefs held that the world was made of elements endlessly divisible. Aristotle argued alchemy above observation and scientific research. He developed this theory with his gold foil experiment. Aristotle contributed to modern atomic theory by introducing alchemy, an ideology that chemists eventually rebelled against. Largely ignored in Athens, Democritus was nevertheless well-known to his fellow northern-born philosopher Aristotle. Rutherford’s atomic theory was that an atom had a central positive nucleus with negative electrons orbiting it. Their hypothesis on atoms is remarkably similar to modern science's understanding of atomic structure, and avoided many of the errors of their contemporaries. His exact contributions are difficult to disentangle from his mentor Leucippus, as they are often mentioned together in texts. The atomic number is the number of protons that is so important to an atom’s identity. What exactly is the modern atomic theory Atoms of one element are the same, according to modern atomic theory, whereas atoms of various elements are different. He was an influential pre-Socratic philosopher who formulated an atomic theory for the cosmos. Aristotle describes his concept of five elements of matter around 340 BCE. Aristotle was the first person to suggest that the world was made up of elements, which he believed to be Earth, Wind, Fire and Water. Aristotle’s life began in 384BC in Stageira, Chalcidice.
He wrote on many subjects including science, logic, philosophy, politics and ethics. He continued the same project of philosophy that Plato was doing, but believed that he was correcting many of Plato’s errors. Aristotle believed that universal forms did not have to be attached to each object or concept, and that every instance of an object or concept had to be examined on its own.Democritus ("chosen of the people") was an Ancient Greek philosopher born in Abdera, Thrace, Greece. Aristotle was a classical Greek philosopher taught by Plato. Plato believed that concepts had a universal and ideal form, which led to his idealistic philosophy. What is the difference between Plato and Aristotle? Instead, he claimed that forms are intrinsic to objects and cannot exist apart from them, so they must be studied in relation to them. The atomic theory has changed over time and many scientists are. By treating different metals and ores, the goal was to change the structure of the item so that it could become more valuable. Ideas, theories, and models in science change over time as new information is learned.

They used Aristotle’s idea about matter and began to create experiments and activities with them. Plato’s theory of forms, which claims that properties like beauty are abstract universal entities that exist independently of the objects themselves, was famously rejected by Aristotle. The alchemists began examining the atomic theory about two centuries after the death of Aristotle. Compounds are formed when atoms are combined in simple ratios to form compound atoms (molecules).
According to the theory, matter is made up of indivisible particles known as atoms, and that all atoms of a given element are identical and cannot be created or destroyed.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
